Troubleshoot Web Browser issues on Windows
Web browser is an essential tools in our daily digital lives, and Microsoft Edge and Google Chrome are among the most popular. However, like any software, they can sometimes encounter issues that disrupt their functionality. Thereafter, this article will guide you through troubleshooting common problems with Microsoft Edge and Google Chrome, helping you resolve issues and maintain a smooth browsing experience.

Reset Microsoft Edge or Chrome Browser
Resetting the Browser means restoring it to its default settings.. This process is a helpful troubleshooting step when it is experiencing issues such as slow performance, unexpected crashes, unusual behaviour, or problems that may have arisen due to misconfigured settings, incompatible extensions, or potential malware interference. Moreover, resetting Edge/Chrome gives it a “fresh start,” which can help resolve a wide range of issues without impacting your personal data.
Purpose of resetting:
- Improves Performance: Resetting the browser can help eliminate factors that slow down performance, such as excessive or corrupted temporary files, overloaded extensions, or conflicting settings.
- Fixes Unusual Behavior: Issues like unresponsive tabs, frequent crashes, or incorrect page displays can often be resolved by resetting the browser.
- Removes Unwanted Changes: If your browser has been altered by a malicious extension or unwanted program, resetting it can remove those unwanted changes.
Steps to Reset the Browser
Subsequently, To Reset Edge or Chrome on Windows, see the steps below:
- Click on the three-dot menu button on the top right, of Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome.
- Click on Settings.
- Click on Reset settings.
- Click on Restore settings to their default values.
- Click on Reset.
Disable browser extensions you have
A browser extension is a small software program that adds specific features or functionalities to a web browser, enhancing or modifying the browsing experience. Moreover, the Extensions can range from simple tools that change the browser’s appearance to more complex applications that interact with web content or provide additional services.
Key Features of Browser Extensions:
- Customization: Extensions allow users to personalize their browser’s functionality. For example, they can change the look , add shortcuts, or modify the way web pages are displayed.
- Enhanced Functionality: Extensions can add new features so that aren’t available by default. So, the examples include ad blockers, password managers, and productivity tools like to-do lists or note-taking apps.
- Security and Privacy: Extensions can enhance security and privacy by adding features like secure browsing, VPNs, or tools that protect against phishing attacks.
Steps to turn off Browser Extensions:
For both Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge, the steps to disable extensions are similar:
- Open the Browser: Launch Google Chrome or Microsoft Edge on your computer.
- Access the Extensions Page:
- Click on the three-dot menu icon located in the upper-right corner of the browser window.
- From the dropdown menu, select
Extensionsor navigate toMore tools>Extensions.
- View Installed Extensions: You’ll see a list of all the extensions currently installed in your browser.
- Disable an Extension:
- Locate the extension you want to disable.
- Toggle the switch next to the extension to turn it off. The switch will change color, indicating that the extension is now disabled.
- Repeat if Necessary: If you suspect multiple extensions are causing issues, repeat the process to disable them all.
- Test Your Browser: After disabling the extensions, try using your browser as you normally would to see if the issue has been resolved. Restart the browser and check.
Disable hardware acceleration in the browser
Hardware acceleration is a feature built into modern web browsers that allows the browser to shift certain tasks, especially those related to rendering graphics, animations, and video playback, from the Central Processing Unit (CPU) to the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) of your computer. Likewise, the GPU is specifically designed to handle such tasks more efficiently, which can lead to a smoother and faster browsing experience. Sometimes, if the GPU has an issue, it may cause issues on your web browser, like a flicker, freeze etc.
Basically, the benefits of Hardware Acceleration are:
- Enhanced Performance: Improves performance for graphically intensive tasks by utilizing the GPU’s capabilities.
- Smoother Experience: Results in smoother video playback, better handling of complex animations, and improved responsiveness for web applications.
- Freed CPU Resources: Allows the CPU to focus on other operations, enhancing overall system performance.
Concurrently, disable this feature using the 3 dots menu.
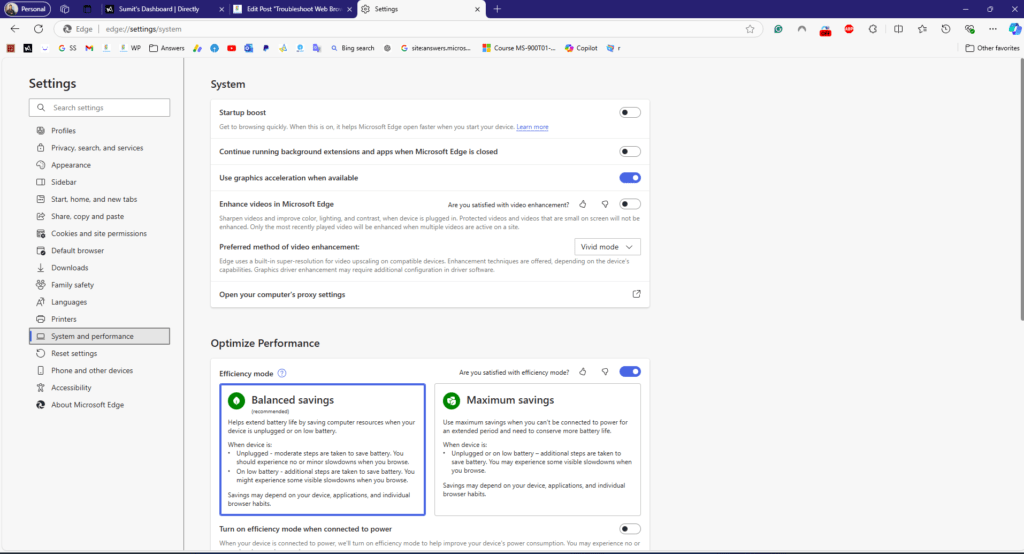
- Open the Settings option.
- Navigate to System
- Turn off Use Hardware/GPU acceleration when available.
Use the Beta version of Chrome or Microsoft Edge to test your issue
Sometimes, the Chrome or Microsoft developers know about an issue you are having with your browser. Concurrently, trying the Beta version of Chrome or Edge is wise to isolate the problem. You can download them using the following links:
Additionally, Beta, aka the preview version of Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome, installs as a separate version so your data on the Retail browser will remain unaffected.
Reinstall Microsoft Edge or Chrome
The last resort is to try reinstalling Microsoft Edge or Chrome.
To download Chrome, you can go to this link.
To summarize, this article can help you troubleshoot issues with your Web Browser based on Chromium.